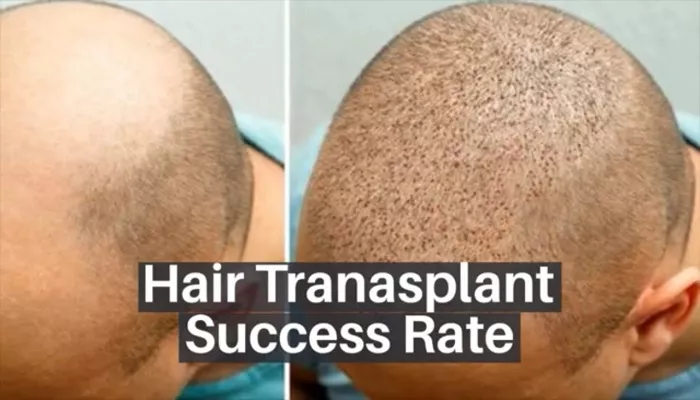
Hair loss can be a distressing experience, but modern hair transplant procedures offer effective solutions. Among the various techniques available, understanding which procedure yields the most successful results is crucial for individuals considering hair restoration. This comprehensive guide explores the most successful hair transplant procedures, analyzing their effectiveness, benefits, and considerations to help you make an informed decision.
What is Hair Transplantation
Hair transplantation involves relocating hair follicles from a donor area (typically the back or sides of the scalp) to areas experiencing hair loss. The primary goal is to achieve natural-looking hair growth that is permanent and sustainable.
Key Hair Transplant Techniques
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
FUT, also known as the strip method, involves removing a strip of scalp from the donor area, dissecting it into individual follicular units, and transplanting them into the recipient area.
Advantages:
- Ability to harvest a large number of grafts in a single session
- Potentially higher graft survival rates
- Cost-effective for extensive hair loss
Considerations:
- Leaves a linear scar at the donor site
- Longer recovery time compared to other methods
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
FUE involves extracting individual hair follicles directly from the donor area and implanting them into the recipient area.
Advantages:
- Minimally invasive with no linear scarring
- Faster recovery time
- Suitable for individuals who prefer short hairstyles
Considerations:
- Longer procedure time
- May be more expensive due to the meticulous nature of the process
Direct Hair Implantation (DHI)
DHI is a variation of FUE where extracted follicles are implanted directly into the recipient area using a specialized tool, without creating prior incisions.
Advantages:
- Precise implantation with controlled depth and angle
- Reduced handling of grafts, potentially increasing survival rates
Considerations:
- Requires specialized equipment and expertise
- May be more costly than traditional FUE
Success Rates of Hair Transplant Procedures
Success in hair transplantation is measured by graft survival rates, natural appearance, and patient satisfaction.
- FUT: Studies indicate a success rate between 95% and 98%, with some cases achieving up to 100% when performed by experienced surgeons.
- FUE: Modern FUE techniques have improved significantly, with success rates comparable to FUT, often reaching around 90% to 95%.
- DHI: DHI’s precision offers high success rates, though comprehensive comparative studies are limited.
Factors Influencing Success
Several factors contribute to the success of a hair transplant:
- Surgeon’s Expertise: The skill and experience of the surgeon play a pivotal role in achieving optimal results.
- Patient’s Health: Overall health, including scalp condition and absence of underlying conditions, affects healing and hair growth.
- Post-Operative Care: Adhering to aftercare instructions ensures proper healing and graft survival.
- Technique Selection: Choosing the appropriate method based on individual needs and hair loss patterns is essential.
Choosing the Right Procedure
Selecting the most suitable hair transplant procedure depends on various factors:
- Extent of Hair Loss: FUT may be preferable for extensive hair loss due to the ability to harvest more grafts.
- Scarring Concerns: FUE and DHI are ideal for those concerned about visible scarring.
- Budget: FUT is generally more cost-effective, while FUE and DHI may be pricier due to their complexity.
- Lifestyle: Individuals desiring minimal downtime may opt for FUE or DHI for their quicker recovery periods.
Conclusion
While all hair transplant procedures have high success rates when performed by qualified professionals, the choice between FUT, FUE, and DHI should be tailored to individual needs, preferences, and specific hair loss conditions. Consulting with a reputable hair restoration specialist is crucial to determine the most effective approach for achieving natural and lasting results.
Related topics: