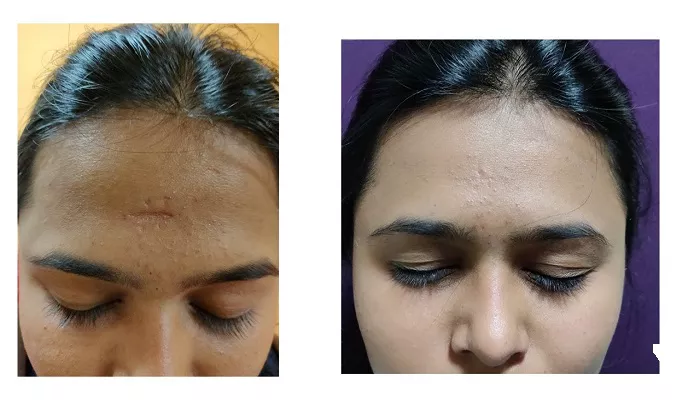
Scar revision is a procedure aimed at improving the appearance of scars, making them less noticeable and more consistent with the surrounding skin. Depending on the scar’s size, location, and complexity, different anesthesia options may be employed to ensure patient comfort and optimal results.
What is Scar Revision
Scar revision can be either surgical or non-surgical. Surgical methods involve removing the scar tissue and rejoining the skin, while non-surgical options include treatments like laser therapy, dermabrasion, and microneedling. The choice of procedure depends on the scar’s characteristics and the desired outcome.
Anesthesia Options for Scar Revision
The type of anesthesia used during scar revision varies based on the procedure’s extent and the patient’s needs. The main anesthesia options include:
Local Anesthesia
Local anesthesia involves numbing the specific area where the procedure will take place. It’s commonly used for minor scar revisions and allows the patient to remain awake during the procedure. This method is often preferred for its minimal side effects and quick recovery time.
Intravenous (IV) Sedation
IV sedation involves administering sedatives through a vein, inducing a state of relaxation and drowsiness. It’s often combined with local anesthesia to ensure comfort during more extensive procedures. Patients may remain conscious but relaxed, with little to no memory of the procedure.
General Anesthesia
General anesthesia renders the patient unconscious during the procedure. It’s typically reserved for extensive scar revisions or when the scar is located in a sensitive area. While it carries more risks than local anesthesia or sedation, it’s sometimes necessary for complex procedures.
Factors Influencing Anesthesia Choice
Several factors determine the appropriate anesthesia type for scar revision:
- Scar Size and Location: Larger or more complex scars may require deeper anesthesia.
- Procedure Complexity: More involved procedures might necessitate sedation or general anesthesia.
- Patient Health and Preferences: A patient’s medical history and comfort level play a role in anesthesia selection.
- Surgeon’s Recommendation: The surgeon’s assessment and experience guide the anesthesia choice.
Preparing for Anesthesia
Before undergoing scar revision, patients should:
- Discuss Medical History: Inform the surgeon of any medical conditions or medications.
- Follow Pre-Operative Instructions: This may include fasting or adjusting medications.
- Arrange Transportation: If sedation or general anesthesia is used, patients should have someone to drive them home.
Post-Procedure Considerations
Recovery varies based on the anesthesia type and procedure complexity:
- Local Anesthesia: Patients can usually return home shortly after the procedure.
- IV Sedation or General Anesthesia: Monitoring in a recovery area is required until the patient is alert.
- Follow-Up Care: Adhering to post-operative instructions ensures proper healing and optimal results.
Conclusion
Anesthesia is a crucial component of scar revision, tailored to the procedure’s demands and the patient’s needs. Understanding the available options and collaborating with a qualified surgeon ensures a comfortable experience and satisfactory outcomes.
Related topics: