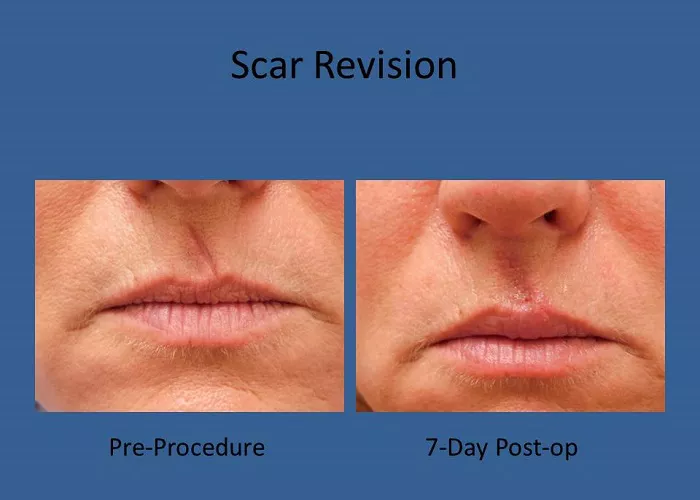
Scar revision surgery is a procedure aimed at improving the appearance of scars, making them less noticeable and more in harmony with the surrounding skin. While the surgical technique plays a crucial role, postoperative care is equally important to ensure optimal healing and results. This guide provides detailed information on what to avoid after a scar revision to promote effective healing and minimize complications.
What is Scar Revision Surgery
Scar revision can be performed using various techniques, including excision, dermabrasion, laser therapy, or skin grafting, depending on the type and location of the scar. The primary goal is to improve the scar’s appearance, but complete removal is often not possible. The success of the procedure largely depends on proper postoperative care.
Immediate Postoperative Care
Rest and Activity
After surgery, it’s essential to get plenty of rest. Avoid strenuous activities and heavy lifting for at least two weeks, as these can increase swelling and risk of bleeding. Light walking is encouraged to promote circulation, but always follow your surgeon’s specific instructions.
Wound Care
Keep the surgical site clean and dry. You may be instructed to gently wash the area with mild soap and water after 24 hours. Avoid submerging the wound in water, such as baths or swimming pools, until cleared by your doctor.
What to Avoid After Scar Revision
1. Smoking
Smoking significantly impairs wound healing by reducing blood flow and oxygen to the tissues. It’s crucial to avoid smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke for at least three weeks post-surgery to minimize the risk of complications.
2. Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol can interfere with the healing process and interact negatively with prescribed medications. Refrain from consuming alcohol for at least two weeks after surgery, or longer if advised by your surgeon.
3. Sun Exposure
Exposing the healing scar to sunlight can lead to hyperpigmentation, making the scar more noticeable. Protect the area by keeping it covered or applying a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher for at least 12 months post-surgery.
4. Vigorous Exercise
Engaging in high-intensity workouts or activities that strain the surgical area can disrupt healing. Avoid such exercises for at least two weeks, or until your surgeon gives clearance to resume normal physical activity.
5. Certain Medications
Some medications, like aspirin and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can increase bleeding risk. Avoid these unless specifically approved by your surgeon. Always inform your doctor about all medications and supplements you’re taking.
6. Touching or Picking at the Scar
Resist the urge to touch, scratch, or pick at the healing scar. Such actions can introduce bacteria, leading to infection, or disrupt the healing process, resulting in a more prominent scar.
7. Tight or Irritating Clothing
Wearing tight clothing over the surgical area can cause friction and irritation. Opt for loose-fitting, breathable fabrics to minimize discomfort and allow proper airflow to the healing site.
8. Skipping Follow-Up Appointments
Regular follow-up visits allow your surgeon to monitor healing and address any concerns promptly. Missing these appointments can delay the identification and management of potential complications.
Additional Tips for Optimal Healing
- Nutrition: Maintain a balanced diet rich in vitamins and proteins to support tissue repair.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to keep your skin hydrated and promote healing.
- Sleep: Ensure adequate rest to allow your body to recover effectively.
- Stress Management: High stress levels can negatively impact healing. Engage in relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation.
Conclusion
Proper postoperative care is vital for the success of scar revision surgery. By avoiding harmful habits and following your surgeon’s instructions diligently, you can enhance healing and achieve the best possible aesthetic outcome. Always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice tailored to your specific situation.
Related topics: